- ...
LAND0.1
-
LAND: Laboratory for Modeling/Analysis and Development
of Computer and Communications Systems.
URL: http://www.land.ufrj.br
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- .../UFRJ0.2
- UFRJ: Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...#tex2html_wrap_inline3807#8.1
- Remeber that
Tangram-II's variables start from
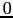 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...trace.txt11.1
- This file is part of MTK, and can be found in
 diretório
X
diretório
X .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... observations11.2
- OK, so this is an unreal number of
observations to collect in a scenario like this, but so is a parrot standing on
top of a casino table, right?
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
gain11.3
- By log-likelihood gain we mean the difference between the
log-likelihood in iteration
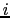 and iteration
and iteration 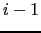 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... group11.4
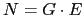
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... group11.5
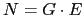
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... transition11.6
- The initial state
in the lower-level chain is chosen according to a initial state probability
distribution associated with this lower-level Markov chain. Keep in mind that
after every transition in the upper-level chain, which includes
transitions to the same state, a new initial lower-level state is chosen, and
the symbol emission process statrs from that state.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... gain11.7
- By log-likelihood gain we mean the
difference between the log-likelihood in iteration
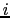 and iteration
and iteration 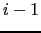 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... group11.8
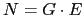
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... group11.9
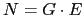
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... transition11.10
- The initial state in the lower-level chain is
chosen according to a initial state probability distribution associated with
this lower-level Markov chain. Keep in mind that after every transition
in the upper-level chain, which includes transitions to the same state, a new
initial lower-level state is chosen, and the symbol emission process statrs
from that state.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... transition11.11
- The initial
state in the lower-level chain is chosen according to a initial state
probability distribution associated with this lower-level Markov chain. Keep in
mind that after every transition in the upper-level chain, which includes
transitions to the same state, a new initial lower-level state is chosen, and
the symbol emission process statrs from that state.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... plugin11.12
- Which can be
found in the $MTK_HOME/plugins directory.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.